Edge Hysteresis Thresholding
The edge magnitude images produced from most real-world images contain spurious or noise edge pixels. Often these edge pixels are the result of video noise, reflections, or other image imperfections. You can eliminate spurious pixels by applying a simple threshold to the edge magnitude image.
Simple edge thresholding often removes actual edges of interest in addition to spurious edges. Because the actual edges of interest in an image are usually composed of a collection of adjacent edge pixels, you can eliminate spurious pixels without eliminating actual edges by applying edge hysteresis thresholding to an edge magnitude image.
Edge hysteresis thresholding eliminates edge pixels that are below a certain magnitude that are not adjacent to other edge pixels above a certain magnitude in the edge magnitude image. This has the effect of preserving the contiguous edge pixels that make up true edges of interest in the image while eliminating edge pixels that have resulted from noise or other image defects.
The figure below shows the effect of edge hysteresis thresholding on an edge magnitude image.
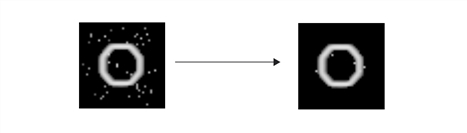
You can apply edge hysteresis thresholding to any edge magnitude image, but best results will be obtained by using one that has been peak-detected. The figure below shows the effect of edge hysteresis thresholding on a peak-detected edge magnitude image.
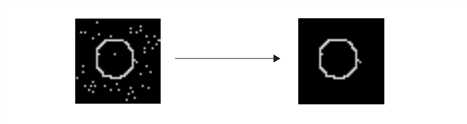
Edge hysteresis thresholding on peak-detected image