Network Settings
- In case of using an In-Sight ViDi PC system, the settings of this utility are available in the Industrial Ethernet utility for configuration.
-
This utility can only be used to configure one device at a time, and is only available when a single device is selected in the In-Sight® Device Pane.
The Network Settings utility configures the network settings of an In-Sight vision system. Perform the following steps to do so:
- Launch In-Sight Vision Suite if it is not already running.
-
Left-click the device you want to configure on the In-Sight® Device Pane on the left. The list of Utilities applicable to the selected vision system then appears at the bottom of the window.
-
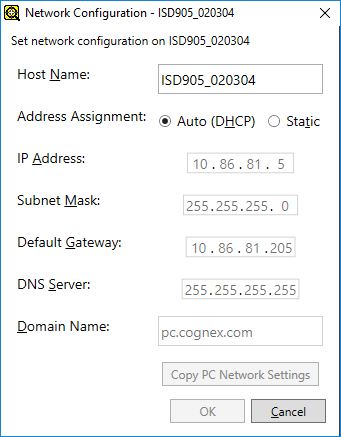
Press the Network Settings button to launch the Network Settings dialog.
-
Adjust the available settings according to the below descriptions:
Property Description Host Name Defines the name of the In-Sight device which will appear both in the In-Sight® Device Pane and in the adapter as well.
Note:- Valid characters for a host name are A -Z (upper and lowercase), 0-9 and hyphen ('-').
- Host names must begin with a letter.
- Host names must be between 1 and 63 characters.
Address Assignment Defines how the device will be assigned its network settings: Auto (DHCP) or Static.
- Auto (DHCP): In-Sight devices that support Ethernet configuration can be set with this option to obtain an IP address dynamically if a DHCP server is available. In this case, any In-Sight Ethernet device can send out a request and receive its network settings (such as an IP address, DNS server, subnet mask, gateway and domain name) automatically.
- Static: This setting allows you to enter network settings manually for every device. This option is preferred when there is a large number of devices present on the network.
Tip: After the initial network configuration is completed, Cognex strongly recommends disabling DHCP on the device(s) and assigning a static IP address to them to prevent intermittent DHCP traffic.Note:- If the Auto (DHCP) setting is selected, all other settings are disabled.
- If the Static setting is selected, you may be able to configure settings that are inconsistent with the subnet settings of the PC running the software. This allows a device to be preconfigured on one network, and then deployed on another network.
IP Address Assigns a unique identifier for each device on the network, which must be consistent with the IP address-numbering scheme of the local network. Subnet Mask Defines which part of the IP address refers to the network and which part refers to the host. The network part of the IP address is the same for all hosts on the same subnet, and the remainder is unique to each host.
An IP address is actually a combination of two addresses: a network address and a host address. The subnet mask defines which part of the IP address refers to the network and which part refers to the host. The network part of the IP address is the same for all hosts on the same subnet, and the remainder is unique to each host.
There are three types (or classes) of subnet masks. The class of a particular subnet on a network is defined by the number of bits used to represent the network and host address portions in the IP address, as shown in the table below:
Class Subnet Mask Network Address Host Address A 255.0.0.0 8 bit 24 bit B 255.255.0.0 16 bit 16 bit C 255.255.255.0 24 bit 8 bit For example, consider a networked In-Sight host system with the IP address 192.168.0.1. If the first three numbers (192.168.0) identify the 24-bit network address, and the last number (1) is the 8 -bit address for the In-Sight host on the network, then the subnet mask for this host is 255.255.255.0.
Default Gateway Specifies the IP address of the gateway host, if available on the network. The gateway host is responsible for relaying data between hosts on different networks.
Tip: A gateway is a device that routes data packets from a device on the local subnet to a device on another subnet. If an In-Sight device needs to communicate with a device on a different subnet, enter the address of the gateway device in the Default Gateway field; otherwise, leave this field blank.DNS Server Specifies the IP address of the host on the network providing DNS resolution, if available.
Note:Host devices on the same network have unique IP address numbers, but a common part of the address is shared by all hosts on the same domain (such as yourdomain.com). These numbers can be difficult to remember, so each host is usually assigned a host name to serve as an "alias" for its IP address. A DNS server translates these host names back into IP addresses that can be understood on the network.
For example, if an In-Sight device with the IP address 192.168.1.2 is named PRODUCTION2, the DNS server knows that PRODUCTION2 actually refers to the In-Sight host at the specified address. The DNS Server field determines which host is contacted (by its IP address) to resolve the translation of host names to IP addresses within the specified domain.
Domain Name Specifies the network domain for the host network.
Note: A domain is a group of devices on a network that share a common part of their IP addresses. A Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) consists of a host name and a domain name, including a top-level domain. For example, www.yourdomain.com is a fully qualified domain name: www is the host, yourdomain is the second-level domain and .com is the top level domain.Copy PC Network Settings Clicking this button will configure the Subnet Mask, Default Gateway, DNS Server, and Domain Name settings to match the PC on which the software is running. This button is only enabled when Address Assignment is set to Static.