Green Classify Focused
Overview of Green Classify Architectures
There are 3 types of architecture in Green Classify Tool: Focused, High Detail, and High Detail Quick.
-
The Green Classify Focused is used to classify an object or a complete scene. Be it the identification of products based on their packaging, the classification of welding seams or the separation of acceptable or unacceptable defects; the Focused mode learns to separate different classes based on a collection of labeled images. To train the Focused mode, all you need to provide are images assigned and labeled the different classes.
-
The Green Classify High Detail is similar with Focused Green Classify Tool, but uses a different architecture. The High Detail mode learns to separate different classes based on a collection of labeled images. To train the High Detail mode, all you need to provide are images assigned and labeled the different classes.
-
The Green Classify High Detail Quick is the modification of Green Classify High Detail mode, hiking up its training speed dramatically with some decrease in detection accuracy. It was forged to import the state-of-the-art training algorithms to guarantee robust and still performing results though its accuracy level is slightly lower than that of Green Classify High Detail. It also requires few Tool Parameters thus offers easy and quick training. The other details including its step-by-step usage are not much different from Green Classify High Detail.
About Green Classify Focused
Green Classify Focused is an image classification tool which learns the pixel information of images that belong to the training set by feature sampling. It nicely can learn image information when your images are correctly labeled, when the ROI (Region of Interest) of your images are correctly set, and when a set of tool parameter values that catch the discriminative features well from the images in the training set are given. After it learns enough, in other words, it is trained enough, it can make a prediction for each image about which one belongs to a certain class.
It samples features from images using a sampler whose sampling magnitude can be defined by users, which is also the case in all other Focused tools in VisionPro Deep Learning. It is quicker than Green Classify High Detail for producing classification results in most environments with serviceable performance.
Architectures: Green Classify Focused vs Green Classify High Detail
Focused mode uses an architecture which is different from High Detail mode. Due to the different architecture, Focused mode takes less time for training than the High Detail, so you can get a fast feedback when compared to High Detail mode.
Focused mode setting is selective, focusing on the parts of the image with useful information. Due to this focus, the network can miss information, especially when the image has important details everywhere.
High Detail mode uses an architecture which is different with Focused mode. Due to the architecture, High Detail mode takes more time for training than the Focused mode, but you can get more accurate results.
The way you create a model in High Detail mode is basically same with Focused mode but there are some differences in tool parameters. Also, you cannot assign multiple tags per view in High Detail mode. Each view has only a single corresponding tag and it means that non-exclusive mode is not supported.
| Focused mode | High Detail mode | |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Fast | Slow |
| Accuracy | Accurate | More Accurate |
| Number of Parameters |
Many |
Many |
| Image Dataset Composition | Training Set, Test Set | Training Set, Validation Set, Test Set |
Architectures: Green Classify Focused vs Green Classify High Detail Quick
Green Classify High Detail Quick mode uses an architecture which is different from that of Focused mode. Due to its architectural difference, it doesn't have Sampling Parameters in Tool Parameters pane as it samples from the entire view. The way you label images and create a neural network model in Green Classify High Detail Quick is basically the same as Focused mode, but it requires almost no parameters compared to Green Classify Focused.
Supported Features vs Architectures
|
Features |
Green Classify Focused | Green Classify High Detail | Green Classify High Detail Quick |
| View Inspector | Supported without heat map | Supported with heat map | Supported with heat map |
| Loss Inspector | Not supported | Supported | Not supported |
| Validation Set | Not used in training | Used in training | Not used in training |
| VisionPro Deep Learning Tool Parameters | Less parameters |
More parameters for control*, |
Almost no parameters |
| Multi-class Classification (Non-Exclusive/Exclusive Mode) |
Supported | Not supported | Not supported |
| Resize Mode | Not supported | Supported | Not Supported |
Training Workflow for Green Classify Focused
When a Green Classify tool is in Green Classify Focused mode, the training workflow of the tool is:
- Launch VisionPro Deep Learning.
- Create a new workspace or import an existing one into VisionPro Deep Learning.
- Collect images and load them into VisionPro Deep Learning.
- Define ROI (Region of Interest) to construct Views.
- If a pose from a Blue Locate tool is being used to transform the orientation of the View being used as an input to the Green Classify tool, process the images (press the Scissors icon) before opening the Green Classify tool. For more details, see ROI Options Following a Blue Locate Tool.
If necessary, adjust the Region of Interest (ROI). Within the Display Area, right-click and select Edit ROI from the menu.

- After adjusting the ROI, press the Apply button and the adjusted ROI will be applied to all of the images.
- Press the Close button on the toolbar to continue.
- If there is extraneous information in the image, add appropriate masks to exclude those areas of the image. Within the Display Area, right-click and select Edit Mask from the menu.
From the Mask toolbar, select and edit the appropriate masks.

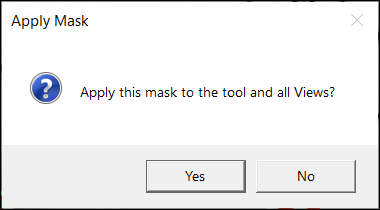
After adding the necessary mask(s), press the Apply button and the mask will be applied to the current image.
If you click Apply All and click Yes button on the ensuing Apply Mask dialog after adding the necessary masks, the same mask will be applied on all the images. If you click No on the dialog, the mask will not be applied and you go back to the Edit Mask window.
- Press the Close button on the toolbar to continue.
-
Go through all of the images and label the images with classification tags. See Create Label (Labeling) for the details of labeling.
Tip: It is recommended to annotate your image files with descriptive names or numbering schemes to help when labeling the images. -
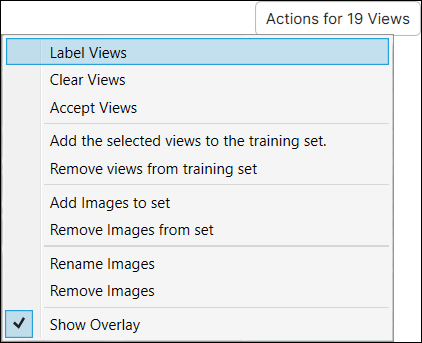
You can use the Label Views option in the View Browser.
-
When labeling, you can either apply a tag or use regular expressions to apply the classification tag label.
- Make sure that all of the images have been labeled with a classification tag.
- Split the entire images into the training images and the test images. Utilize image sets to properly divide them into the training and test group. Add images to the training set.
- Select the images in the View Browser, and on the right-click pop-up menu click Add views to training set. To select multiple images in the View Browser, use the Shift + Left Mouse Button.
- Or, use Display Filters to show the desired images for the training only and add them to the training set by clicking Actions for ... views → Add views to training set.
- Prior to training, you need to set parameters in Tool Parameters. You can configure Training, Sampling, and Perturbation parameters or just use the default values of these. See Configure Tool Parameters for the details of the supported parameters.
- Ensure that the Feature Size parameter in Sampling parameters has been set. The Feature Size parameter gives the network a clue to the size of the features that you are interested for classification. So, if the Feature Size parameter setting is larger than the features in your application, there is a good chance the tool will not determine the correct class for your image.
- You can set the Feature Size by either manually adjusting the parameter value, or graphically by re-sizing the interactive Feature Size graphic.
- If you want more granular control over training or processing, turn on Expert Mode on Help menu to initialize additional parameters in Tool Parameters.
- Train the tool by pressing the Brain
icon.
- If you stop training in the middle of it by pressing the Stop
 icon, you can stop training but you will lose the current tool so far trained.
icon, you can stop training but you will lose the current tool so far trained.
- If you stop training in the middle of it by pressing the Stop
-
After training, review the results. Open Database Overview panel and review the Confusion Matrix and Precision, Recall, F-Score for each class (tag) to understand the results. See Interpret Results for the details of interpreting results.
- After reviewing the results, go through all of the images and see how the tool correctly or incorrectly marked the tags for each image.
- If the tool has correctly marked the images with the appropriate tag, right-click the image and select Accept View.
- If the tool has incorrectly marked the images with incorrect tags:
- Right-click the image again and select Clear Markings and Labels.
Manually tag the image.

If you encountered the scenario in (a.), you are ready to use the tool. If you encountered the scenario in (b.), you will need to retrain the tool and repeat the steps 11 ~ 14.
The details of each step are explained in each subsection of Training Green Classify Focused.